Check the specifications and configurations available in the Patrika 325 - N100 plugin below:
Available from version: Plugin Builder 1.60.17.5
Machine type: CNC Machining
Manufacturer: Morbidelli | SCM
Generated file extension: .pgmx and .xcs, when the Genio integration system is selected, the generated format is .pgm.
Main Features
- Drilling
- Canals
- Machining
File
Defines which columns go into the Nesting file. For more information, click here.
Standard items in the export to be executed, there is no need to add more items, as only the pre-registered items are read.
Label
Label size configuration, millimeters or pixels can be used.
IMPORTANT: The maximum size of the label must be respected, the items that make it up are not configurable nor are their model.
Maquina 1
General
Name: define the name for the machine.
IMPORTANT: the name defined in this field also changes the name of the folder where the generated files will be saved.
Length X (mm): length of the machine.
Width Y (mm): width of the machine.
IMPORTANT: Starting from version 1.60.18.2 of the Plugin Builder, the PAN format has been added for file generation.
Blocking option (V): V command in the header that defines suction and vacuum locking options.
T for bined area field: T command in the header for combined area work fields.
T to the field with individual area: T command in the header for individual area work fields.
Integration System
Integration System: Defines the integration system for which the programs will be generated.
Options: Genio, Maestro, or Maestro with Label.
Setups
General
Name: the name set in this field also changes the name of the folder where the generated files will be saved.
Alignment by face: defines whether the alignment face registered on each part is considered when generating programs. If yes, this face will be aligned according to the selected configuration. For more information click here.
Perform drilling: machine is enabled to drill holes.
Make slots: with the option checked the registered slot will be generated in the machine programs.
Perform machining: with the option checked the registered machining operations will be generated in the machine programs.
Make profile machining: with the option checked, the registered profile machining operations are generated in the machine programs. For more information click here.
Variable usage field distance, in the X axis: distance from the end of the part on the X axis, which determines the area (blue area on the image) where operations should take variable part size minus the distance from the operation under consideration to the end.
Variable usage field distance, in the Y axis: distance from the end of the part on the Y axis, which determines the area (red area on the image) where operations should take variable part size minus the distance from the operation under consideration to the end.
Invert variable fields: by checking this option, when a rotated part is generated, the fields invert as shown in the picture.
Consider grain direction: consider grain direction when generating Nesting programs.
Machining processes: How the machine processes machining.
Perform machined contour: defines the contour of which parts will be generated.
- None: contour machining will not be generated for any part;
- All: contour machining will be generated for all parts;
- Only marked: contour machining will be generated only for parts that have the Machined Contour property enabled in the library register.
Perform Nesting: generate programs for Nesting.
Machine
Priorization order: defines the order of prioritization of operations for program generation. According to the order indicated in this field the plugin will prioritize in program A the selected option. Example: In a part that has holes on one side and tears on the other side, the order indicated in this field will determine which of them will be prioritized in the A program.
Slot tool: tool used for slots. IMPORTANT: This option is available when the Make Slots option is selected.
Machining tool: tool used for machining. IMPORTANT: this option is only available when the Machining option is selected.
Operations ordering: order that the machine performs operations. Example: in a part that has holes and tears on the same face the order indicated in this field will determine the sequence in which they will be executed by the machine.
Profile machining tool: this option is only available when the Make Profile Machining option is selected. For more information click here.
File .inf
Detail all programs operations: detail operations not performed in the .inf file in all programs (A, B. C .....).
Generate empty parts info: generate .inf file of parts without operations.
Holes
Drill bits for blind hole operation: option for normal drilling. Normal drilling is considered normal when it is not through or marking drilling.
Drill Bits for through hole operations: type of drill for through hole drilling - Normal Drill, Spear or Reaming Drill.
Drill bit for marking hole operation: type of drill bit for marking drilling – Normal Drill, Lance or Reamer
Depth of marking hole operation (mm): maximum depth to be a marking hole. When the hole is smaller or equal it will automatically be considered a marking hole.
Drill bit angle used in through holes: determine the drill bit end angle for through hole usage (from 25 to 90 degrees). This value is used in the calculation to determine the increment in the through-hole depth to ensure that the hole passes completely through the part.
Drill GAP in through hole operation (mm): determine the clearance of the drill for use in through holes.
Drill Bits Type: defines the codes used for each drill type. The codes are defined in the fields, reamer drill type, lance drill type, normal drill type, and large normal drill type.
Number of horizontal drill bits (X): the number of drills, for each horizontal face, present in the machine.
Number of lateral drill bits (Y): number of drill bits, for each side face, present in the machine.
Slot tool: tool used for tears.
Machining tool: tool used for machining.
Prioritization order: defines the order of prioritization of operations for generating programs.
Operations Ordering: the order in which the machine performs operations.
Profile Machining Tool:
File .inf
Detail all programs operations: detail operations not performed in the .inf file in all programs (A,B,C....).
Generate empty parts info: generate .inf file of parts without operations.
Holes
Drill bits for blind hole operation: option for normal drilling. Normal drilling is considered normal when it is not through or marking drilling.
Drill Bits for through hole operations: type of drill for through hole drilling - Normal Drill, Spear or Reaming Drill.
Drill bit for marking hole operation: type of drill bit for marking drilling – Normal Drill, Lance or Reamer
Depth of marking hole operation (mm): maximum depth to be a marking hole. When the hole is smaller or equal it will automatically be considered a marking hole.
Drill bit angle used in through holes: determine the drill bit end angle for through hole usage (from 25 to 90 degrees). This value is used in the calculation to determine the increment in the through-hole depth to ensure that the hole passes completely through the part.
Drill GAP in through hole operation (mm): determine the clearance of the drill for use in through holes.
Drill Bits Type: defines the codes used for each drill type. The codes are defined in the fields, reamer drill type, lance drill type, normal drill type, and large normal drill type.
Maximum diameter of horizontal drill bit (mm): maximum diameter of horizontal drills.
Maximium diameter of vertical drill bit (mm): maximum diameter of vertical drills.
Maximium drilling depth (mm): maximum depth the drill bit can drill.
Minimium diameter of drill bit (mm): minimum drilling diameter.
Number of horizontal drill bits (X): the number of drills, for each horizontal face, present in the machine.
Number of lateral drill bits (Y): number of drill bits, for each side face, present in the machine.
Number of vertical drill bits (Z): number of vertical drills present in the machine.
Machinings
Execute multiple passes machining in a single machining command: enables the command of multiple passes in a single command.
Inverted Pass: Reversed pass used in edge-side exit operations.
Machining Type: Defines the behavior of through machining. Standard follows the operation registration.
Slots
Maximum slot depth: maximum depth of the slot (groove) in millimeters.
Technical Data
Head displacement over X axis: displacement of the head after operations, so as not to be above the workpiece, in millimeters. The set value will be added to the measurement (X) of the part, if this sum exceeds the allowed value, the maximum displacement of the head in (X) will be considered.
Maximum head displacement over X axis: maximum value that the head can displace over (X) axis after operations.
Maximum thickness(Z): maximum thickness of the part that the machine can perform operations.
Minimum length (X): minimum thickness of the part that the machine can perform operations.
Minimum thickness (Z): minimum thickness of the part that the machine can perform operations.
Minimum width (Y): minimum part length for the machine to perform operations.
Use PARK function: when using the PARK function, it disables the head displacement in X.
Conical Mills
Contour Machining
External contour cut direction: it defines the machining of contours to be made in a non-clockwise or anti-clockwise direction.
Internal Milling
Internal contour machining start: defines where the internal contour machining starts, at one of the corners or in the middle of one of the machining edges.
Internal milling cut direction: it defines the machining of contours to be made in a non-clockwise or anti-clockwise direction.
Properties
Code: tool code.
Cutting Angle: tool cutting angle
Diameter (mm): tool diameter.
Height (mm): tool height.
Horizontal step depth (mm): depth of the tool's step.
Machining Compensation: compensation for drilling and through machining.
Name: tool name
Suction hood position: this value ranges from 0 (no hood positioning) to the value corresponding to the lowest hood position.
Vertical step depth (mm): depth of the tool's step.
Mills
The mills are used to perform slotting and machining.
Contour Machining
Start of contour machining: defines where the contour machining begins, at one of the corners or in the middle of one of the edges of the workpiece. This option is applicable only to external contour machining.
External contour cut direction: it defines the machining of contours to be made in a non-clockwise or anti-clockwise direction.
Internal Milling
Internal contour machining start: defines where the internal contour machining starts, at one of the corners or in the middle of one of the machining edges.
Internal milling cut direction: it defines the machining of contours to be made in a non-clockwise or anti-clockwise direction.
Use cutting direction in single-line operations: when selecting this configuration, single-line machining will start to follow the cutting direction of the cutter.
Lead In
Input type in linear machining: defines the type of input the tool will use when machining and contouring linear forms. Options Ramp, vertical, circular.
- Circular: in this type the tool descends outside the part and then starts cutting tangentially before entering the part.
- Vertical: in this type the tool descends vertically onto the workpiece and begins cutting.
- Ramp: in this type the tool descends by making a ramp until it reaches the maximum depth of operation.
Lead in extension (mm): entry elongation before starting contour cutting, equivalent to the red line in the image.
Ramp lead in extension (mm): input extension used to calculate the ramp input of the tool, equivalent to the red line in the image.
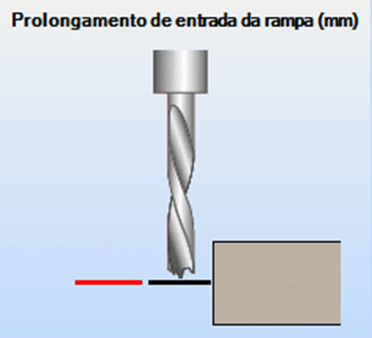
Lead in/ Lead out
Distance between Lead In and Lead Out (mm): distance the tool exits and enters the part. It is advisable that this value be greater than zero so that the cut does not leave any fragments (burrs).
Lead Out
Lead out extension (mm): extension of the exit after finishing machining/contour, equivalent to the red line.
Lead Out type: defines the type of exit the tool will use when performing machining and contouring.
- In the vertical type, the tool descends vertically onto the workpiece and begins the cut.
- In the circular type, the tool descends outside the workpiece and then starts to cut tangentially before entering the workpiece.
- In the ramp type, the tool descends like a ramp and begins the cut.
Ramp lead out extension (mm): extension of the exit after finishing machining/contour, equivalent to the red line in the image.
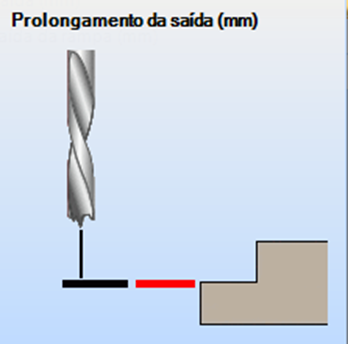
Properties
Height (mm): tool height.
Code: the code defined in this field must be the same as the one defined on the machine so that the tool can be located correctly.
Through plunge and milling offset (mm): compensation of the drilling and machining of the part.
Diameter (mm): tool diameter.
Name: the name defined in this field must match the registration defined on the machine so that the tool can be located correctly.
Suction hood position: this value ranges from 0 (no hood positioning) to the value corresponding to the lowest hood position.
Step depth (mm): depth of tool step.
Overlap (mm): overpass between tool passes to avoid material leftovers.
Tool compensation
Milling alignment: defines if the tool has compensation, Automatic, Center, Left, or Right according to the cutting direction option for contour machining. For more information, click here.
Saws
Saws are used to make slot.
Properties
Alignment: alignment of the saw in each piece.
Code: the code defined in this field must match the registration defined on the machine so that the tool can be located correctly.
Diameter (mm): tool diameter.
Name: the name defined in this field must match the registration defined on the machine so that the tool can be located correctly.
Overlap (mm): input compensation of the saw to perform the cut, in millimeters. This setting is only applied if the slot starts outside or on the starting point of the part.
Suction hood position: this value ranges from 0 (no hood positioning) to the value corresponding to the lowest hood position.
Thickness (mm): thickness of the saw.
Restrictions
Maximum saw thickness: maximum saw thickness.
Minimum saw thickness: minimum saw thickness.
Working Areas
The work areas consist of dividing the table of a machine into specific areas. This facilitates the work of the machine operator, reduces the working area, positioning of work stops, and organization of pieces. For more information, click here.